-
Knee Arthroscopy
Knee arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure performed using an arthroscope, a viewing instrument, to diagnose or treat a knee problem. It is a relatively safe procedure and you will usually be discharged from the hospital on the same day of surgery.
-
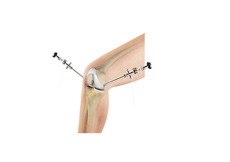
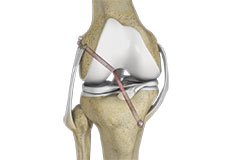
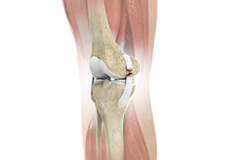
ACL Reconstruction
ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) reconstruction is a commonly performed surgical procedure. With recent advances in arthroscopic surgery, it can now be performed with minimal incision and low complication rates.
-
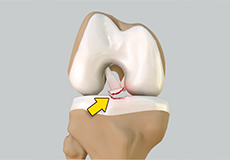
Meniscal Surgery
Meniscal surgery is a surgical procedure employed for the treatment of torn or damaged meniscal tissues in the knee. It is mostly performed as a minimally invasive keyhole procedure.
-
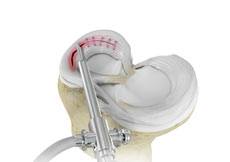
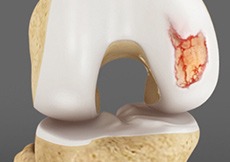
Knee Cartilage Restoration
Knee cartilage restoration is a surgical technique to repair damaged articular cartilage in the knee joint by stimulating new growth of cartilage or by transplanting cartilage into areas with defects in order to relieve pain and restore normal function to the knee.
-
Patellar Tendon Repair
Patellar tendon repair is the surgery performed to reattach the torn tendon to the kneecap and to restore normal function in the affected leg.
-
PCL Reconstruction
PCL reconstruction surgery is a procedure to correct torn posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) in the knee using a tissue graft taken from another part of the body, or from a donor.
-
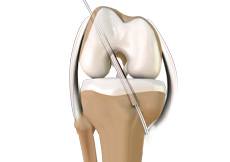
Knee Ligament Reconstruction
Knee ligament reconstruction is a surgical procedure to repair or replace damaged ligaments of the knee joint. The surgery can be performed using minimally invasive techniques.
-
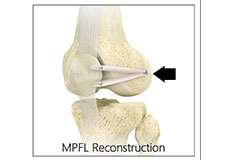
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction
The medial patellofemoral ligament is a band of tissue that extends from the femoral medial epicondyle to the superior aspect of the patella. It is a major ligament that stabilizes the patella and helps in preventing patellar subluxation (partial dislocation) or dislocation.
-
Physical Therapy for Knee
Physical therapy is an exercise program that helps you to improve movement, relieve pain, encourage blood flow for faster healing, and restore your physical function and fitness level. It can be prescribed as an individual treatment program or combined with other treatments.
-
Patellar Instability
Any damage to the supporting ligaments may cause the patella to slip out of the groove either partially (subluxation) or completely (dislocation). This misalignment can damage the underlying soft structures such as muscles and ligaments that hold the kneecap in place.
-
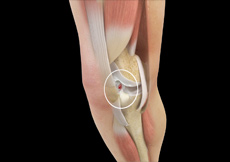
Multiligament Knee Injuries
Injury to more than one knee ligament is called a multiligament knee injury and may occur during sports or other physical activities.
-
Patellofemoral Instability
Patellofemoral instability means that the patella (kneecap) moves out of its normal pattern of alignment. This malalignment can damage the underlying soft structures such as muscles and ligaments that hold the knee in place.
-
Knee Ligament Injuries
Knee problems may arise if any of these structures get injured by overuse or suddenly during sports activities. Pain, swelling, and stiffness are the common symptoms of any damage or injury to the knee.
-
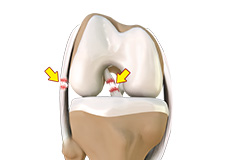
Articular Cartilage Injury
Articular or hyaline cartilage is the tissue lining the surface of the two bones in the knee joint. Cartilage helps the bones move smoothly against each other and can withstand the weight of the body during activities such as running and jumping.
-
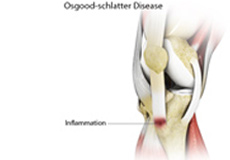
Osgood Schlatter Disease
Osgood-Schlatter disease refers to a condition in older children and teenagers caused by excessive stress to the patellar tendon (located below the kneecap). Participants in sports such as soccer, gymnastics, basketball, and distance running are at higher risk for this disease.
-
Women and ACL Injuries
The anterior cruciate ligament is one of the four major ligaments of the knee that connects the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone) and helps stabilize the knee joint.
-
Knee Sports Injuries
Trauma is any injury caused during physical activity, motor vehicle accidents, electric shock, or other activities. Sports trauma or sports injuries refer to injuries caused while playing indoor or outdoor sports and exercising.
-
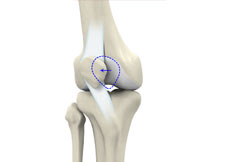
Tibial Eminence Fracture
The tibial eminence, also called the tibial spine, is a bony protuberance of the tibia (shin bone) that attaches to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) of the knee joint.
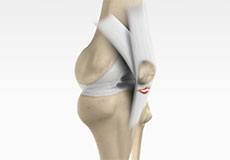
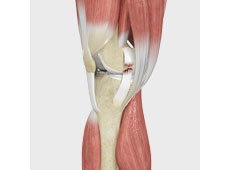
Knee Anatomy
The knee is a complex joint made up of different structures - bones, tendons, ligaments, and muscles. They all work together to maintain the knee’s normal function and provide stability to the knee during movement.
Having a well-functioning healthy knee is essential for our mobility and ability to participate in various activities. Understanding the anatomy of the knee enhances your ability to discuss and choose the right treatment procedure for knee problems with your doctor.
Bones of the Knee
The knee is a hinge joint made up of two bones, the thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia). There are two round knobs at the end of the femur called femoral condyles that articulate with the flat surface of the tibia called the tibial plateau. The tibial plateau on the inside of the leg is called the medial tibial plateau and on the outside of the leg, the lateral tibial plateau.
The two femoral condyles form a groove on the front (anterior) side of the knee called the patellofemoral groove. A small bone called the patella sits in this groove and forms the kneecap. It acts as a shield and protects the knee joint from direct trauma.
A fourth bone called the fibula is the other bone of the lower leg. This forms a small joint with the tibia. This joint has very little movement and is not considered a part of the main joint of the knee.
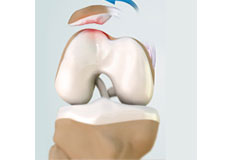
Articular Cartilage and Menisci of the Knee
Movement of the bones causes friction between the articulating surfaces. To reduce this friction, all articulating surfaces involved in the movement are covered with a white, shiny, slippery layer called articular cartilage. The articulating surface of the femoral condyles, tibial plateaus and the back of the patella are covered with this cartilage. The cartilage provides a smooth surface that facilitates easy movement.
To further reduce friction between the articulating surfaces of the bones, the knee joint is lined by a synovial membrane that produces a thick clear fluid called synovial fluid. This fluid lubricates and nourishes the cartilage and bones inside the joint capsule.
Within the knee joint, between the femur and tibia, are two C-shaped cartilaginous structures called menisci. Menisci function to provide stability to the knee by spreading the weight of the upper body across the whole surface of the tibial plateau. The menisci help in load-bearing i.e. it prevents the weight from concentrating onto a small area, which could damage the articular cartilage. The menisci also act as a cushion between the femur and tibia by absorbing the shock produced by activities such as walking, running and jumping.
Ligaments of the Knee
Ligaments are tough bands of tissue that connect one bone to another bone. The ligaments of the knee stabilize the knee joint. There are two important groups of ligaments that hold the bones of the knee joint together, collateral and cruciate ligaments.
Collateral ligaments are present on either side of the knee. They prevent the knee from moving too far during side to side motion. The collateral ligament on the inside is called the medial collateral ligament (MCL) and the collateral ligament on the outside is called the lateral collateral ligament (LCL).
Cruciate ligaments, present inside the knee joint, control the back-and-forth motion of the knee. The cruciate ligament in the front of the knee is called anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the cruciate ligament in the back of the knee is called posterior cruciate ligament (PCL).
Muscles of the Knee
There are two major muscles in the knee - the quadriceps and the hamstrings, which enable movement of the knee joint. The quadriceps muscles are located in front of the thigh. When the quadriceps muscles contract, the knee straightens. The hamstrings are located at the back of the thigh. When the hamstring muscles contract, the knee bends.
Tendons of the Knee
A tendon is a tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone. The quadriceps muscles of the knee meet just above the patella and attach to it through a tendon called the quadriceps tendon. The patella further attaches to the tibia through a tendon called the patella tendon. The quadriceps muscle, quadriceps tendon, and patellar tendon all work together to straighten the knee. Similarly, the hamstring muscles at the back of the leg are attached to the knee joint with the hamstring tendon.